Locations.
In the 1970s, marine dead zones were first noted in areas where intensive economic use stimulated "first-world" scientific scrutiny: in the U.S. East Coast's Chesapeake Bay, in Scandinavia's strait called the Kattegat, which is the mouth of the Baltic Sea and in other important Baltic Sea fishing grounds, in the Black Sea, (which may have been anoxic in its deepest levels for millennia, however) and in the northern Adriatic.
Other marine dead zones have apparently appeared in coastal waters of South America, China, Japan, and southeast Australia. A 2008 study counted 405 dead zones worldwide.
Other marine dead zones have apparently appeared in coastal waters of South America, China, Japan, and southeast Australia. A 2008 study counted 405 dead zones worldwide.
Oregon
Sediment from the Mississippi River carries fertilizer to the Gulf of MexicoOff the coast of Cape Perpetua, Oregon, there is also a dead zone with a 2006 reported size of 300 square miles (780 km²). This dead zone only exists during the summer, perhaps due to wind patterns.
Gulf of Mexico
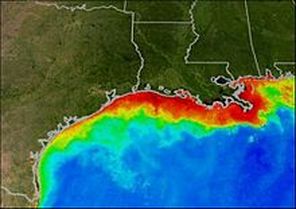
The dead zone of the Gulf of Mexico
Currently the most notorious dead zone is a 22,126 square kilometre (8,543 mi²) region in the Gulf of Mexico, where the Mississippi River dumps high-nutrient runoff from its vast drainage basin, which includes the heart of U.S. agribusiness, the Midwest. The drainage of these nutrients are affecting important shrimp fishing grounds. This is equivalent to a dead zone the size of New Jersey.
There is some concern that the Deep water Horizon oil spill from April to July 2010 may have significantly affected the dead zone. However Terry Hazen, a microbial ecologist with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, has suggested that the oil released from the spill did not travel far enough west in appreciable quantities to affect the current size of the dead zone.
A dead zone off the coast of Texas where the Brazos River empties into the Gulf was also discovered in July 2007.
There is some concern that the Deep water Horizon oil spill from April to July 2010 may have significantly affected the dead zone. However Terry Hazen, a microbial ecologist with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, has suggested that the oil released from the spill did not travel far enough west in appreciable quantities to affect the current size of the dead zone.
A dead zone off the coast of Texas where the Brazos River empties into the Gulf was also discovered in July 2007.
Go to: Related News
